
Stimulant use disorder (StimUD) is a substance use disorder involving any of the class of drugs that include cocaine, methamphetamine, and prescription stimulants. Stimulant use is increasing the United States.
According to the most recent data available from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH), in 2022:
- An estimated 4.6 million people aged 12 or older misused prescription stimulants in the past year.
- Young adults aged 18 to 25 continue to have the highest rates of prescription stimulant misuse..
- Approximately 2.8 million people aged 12 or older used methamphetamine in the past year, reflecting a steady increase compared to prior years.
- 1.7 million people aged 12 or older used cocaine in the past year, which shows a slight decline from previous years
Misused Prescription Stimulants in 2022
2000000
Used Methamphetamine in 2022
1000000
Used Cocaine in 2022
0
Stimulant Use Disorder Resources
Websites
Stimulant Abuse: Signs, Effects, and Treatment Options
This medically reviewed and evidence-based information from American Addiction Centers contains a broad overview of stimulants, including various types and effects, their addictive potential, and treatment options for stimulant misuse.
Get the facts on Stimulant Use Disorder
Stimulant use disorder (StimUD) is a substance use disorder involving any of the class of drugs that include cocaine, methamphetamine, and prescription stimulants.
Tools & Resources
What The Cut: Reno’s Drug Checking Program
What The Cut is a free, confidential drug checking project in Reno, Nevada that analyzes small samples to show people what is actually in the local drug supply. The site shares community testing results, trends, and safety information to help people stay informed and reduce risks.
SafeSpot
SafeSpot is a free, 24/7, national hotline that is staffed by a dedicated team of people with lived and living experience with overdose and drug use. The number one risk factor for fatal overdose is using alone and we are there for you when others cannot be. SafeSpot connects people who are using drugs with a trained operator who can call for help in case of overdose.
Empowered (Roseman University College of Medicine)
Empowered supports pregnant and postpartum individuals in Southern & Northern Nevada (and Weber & Davis Counties in Utah) who use, or have used, opioids or stimulants. Their team provides peer recovery support, care management, and community navigation to help individuals prepare for birth and thrive as caregivers.
Start Your Recovery Nevada Treatment Locator
Start Your Recovery recently developed a comprehensive directory of support resources in Nevada where individuals can: Find local treatment options vetted by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration; Filter to find free and low-cost support options; and Find support groups and other important non-clinical resources.
Nevada Fentanyl Test Strip Finder
A list and map of Fentanyl Test Strip Distribution Sites in Nevada.
Nevada Overdose Reversal Medication Finder
Find naloxone and overdose reversal medications in Nevada.
U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs: Stimulant Use Disorder
Information on stimulant use disorder from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Stimulant Guide
This guide will answer some common questions about stimulants, stimulant use, stimulant overdose, and stimulant overdose prevention strategies developed by harm reduction experts. Straightforward and concise answers are provided in an effort to convey the same key information to a variety of audiences. This document does not contain medical advice, nor should it be referred to in case of emergency. It is purely informational.
Never Use Alone
Toll-free national overdose prevention, detection, life-saving crisis response and medical intervention services for people who use drugs while alone. Never Use Alone’s peer operators are available 24-hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year.
Las Vegas Harm Reduction Center
Trac-B seeks to improve the quality of life of those affected by substance use disorders including our clients, their loved ones, and their communities. Trac-B Exchange provides harm reduction services and supplies to people engaged in the sex trade and people who are injecting or misusing drugs or other substances and are at risk for violence and communicable diseases including Hepatitis C and HIV.
Posters & Infographics

How to use Fentanyl Test Strips – Amphetamines & MDMA Infographic Guide
This is a comprehensive guide to testing Amphetamine like & MDMA like substances for fentanyl using WiseBatch Fentanyl Test Strips.
Get the Guide

Stimulant Trifold Brochures
Stimulant Information Brochures for Providers or Consumers help educate on stimulants, including the effects of stimulants use, pregnancy and stimulant use, and treatment options for persons using stimulants.
Download or request free hard copies

Drug Fact Sheet: Stimulants
This fact sheet from the DEA contains information on what stimulants are, common street names, how they are abused, their effect on the body, and their overdose effects.
Download the fact sheet
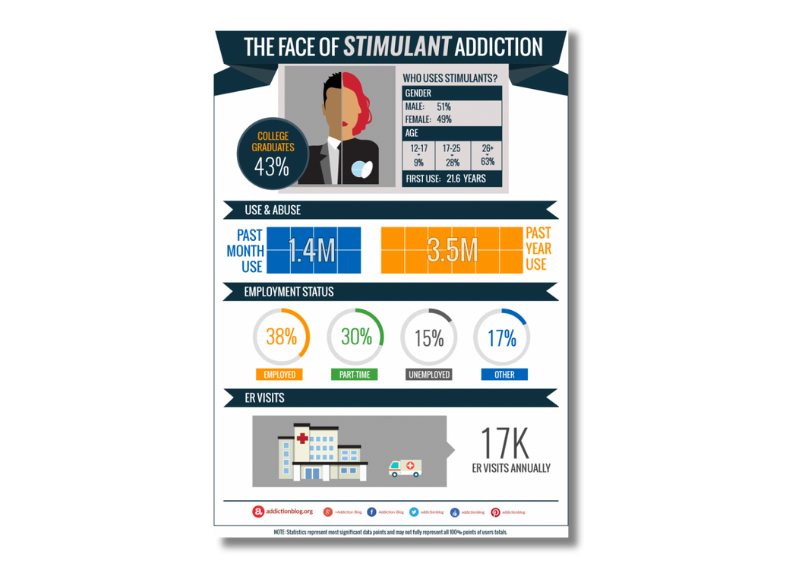
The face of stimulant addiction: Who uses stimulants? (Infographic)
What does the typical stimulant user look like? In this infographic you can explore the age, gender, past year and past month meth use, polydrug use statistics, and emergency room visits.
View the infographic
Publications
The ASAM/AAAP Clinical Practice Guideline on the Management of Stimulant Use Disorder
SAMHSA’s TIP 33: Treatment for Stimulant Use Disorders
This TIP reviews what is known about treating the medical, psychiatric, and SUD-related problems associated with the use of cocaine and methamphetamine, as well as the misuse of prescription stimulants. The TIP offers recommendations on treatment approaches and maximizing treatment engagement and retention, and strategies for initiating and maintaining abstinence.
SAMHSA’s Evidence-Based Resource Guide Series: Treatment of Stimulant Use Disorders
This guide supports health care providers, systems, and communities seeking to treat stimulant use disorders. It describes relevant research findings, examines emerging and best practices, identifies knowledge gaps and implementation challenges, and offers useful resources.
The ASAM/AAAP Clinical Practice Guideline on the Management of Stimulant Use Disorder
Developed by ASAM and AAAP, this guideline focuses on the identification, diagnosis, treatment, and promotion of recovery for patients with stimulant use disorder, stimulant intoxication, and stimulant withdrawal.
Frontline: Meth and the Brain
In this audio slideshow, Dr. Rawson explains how meth affects the brain's dopamine receptors, causing the intense pleasure associated with a meth rush and yet eventually making it impossible for the user to experience an pleasure at all. Richard A. Rawson, Ph.D is an Adjunct Associate Professor in the Department of Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences at the David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California at Los Angeles.
Wound Care & Medical Triage for People Who Use Drugs and the Programs That Serve Them
This comprehensive guide provides information and recommendations regarding general health, safer use practices, common viral, fungal, parasitic, and other injection-related infections, overdose and overamp, tapering, withdrawal, medications for opioid use disorder, and seeking medical care.
Webinars & Online Learning
Current News & Research
Project AMPED
This is a multi-year, mixed methods study in Nevada and New Mexico is examining the patterns, reasons for, and health concerns related to methamphetamine use and opioid use.
Reduced drug use is a meaningful treatment outcome for people with stimulant use disorders (January 10, 2024)
NIH-supported findings suggest the need to expand definitions of addiction treatment success beyond abstinence.
Role of natural products in mitigation of toxic effects of methamphetamine: A review of in vitro and in vivo studies
Methamphetamine (METH) increases dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin concentrations in the synaptic cleft, and induces hyperactivity. The current management of acute METH poisoning relies on supportive care and no specific antidote is available for treatment. The main objective of this review was to present the evidence for effectiveness of the herbal medicine in alleviating the adverse effects of METH abuse.
What The Cut: Reno’s Drug Checking Program
What The Cut is a free, confidential drug checking project in Reno, Nevada that analyzes small samples to show people what is actually in the local drug supply. The site shares community testing results, trends, and safety information to help people stay informed and reduce risks.
