Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) refer to traumatic or stressful events occurring during childhood that can have negative impacts on a person’s physical and mental health later in life. These experiences can include various forms of abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction. The original ACEs study conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and Kaiser Permanente in the 1990s identified ten types of adverse childhood experiences:
- Physical Abuse: Physical abuse involves the intentional use of force that results in injury, pain, or impairment.
- Sexual Abuse: Sexual abuse involves any sexual activity with a child, including molestation, rape, or exploitation.
- Emotional Abuse: Emotional abuse refers to behaviors such as verbal assaults, threats, rejection, and intimidation that undermine a child’s sense of self-worth and emotional well-being.
- Physical Neglect: Physical neglect occurs when a caregiver fails to provide a child’s basic needs, such as food, shelter, clothing, or medical care.
- Emotional Neglect: Emotional neglect involves the failure to meet a child’s emotional needs, such as affection, attention, and nurturance.
- Household Substance Abuse: Exposure to household substance abuse refers to living with a caregiver who abuses alcohol or drugs, which can create an unstable and unsafe environment for a child.
- Household Mental Illness: Living with a caregiver who has untreated mental illness can expose a child to emotional instability, neglect, or abuse.
- Household Domestic Violence: Witnessing domestic violence between caregivers can cause trauma and emotional distress for a child, even if they are not directly abused.
- Parental Separation or Divorce: Separation or divorce can disrupt a child’s sense of security and stability, leading to emotional distress and behavioral problems.
- Incarceration of a Household Member: Having a household member incarcerated can result in loss of support, financial instability, and emotional trauma for a child.
The ACEs study found a strong correlation between exposure to ACEs and negative health outcomes later in life, including chronic physical conditions, mental health disorders, substance abuse, and interpersonal difficulties. Additionally, individuals with a higher number of ACEs are at increased risk for a range of adverse outcomes, highlighting the importance of addressing childhood trauma and providing early intervention and support for affected individuals.
Resources Related to Adverse Childhood Experiences
Websites
Nevada Essentials for Childhood
Take the ACE Quiz – And Learn What It Does and Doesn’t Mean
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
Tools & Resources
Community Resiliency Model (CRM) Overview and Skills Guide
ACEs, Overdose and Suicide Prevention
ACE Interface: The Adverse Childhood Experiences Study
Adverse Childhood Experiences and the Role of Substance Misuse Prevention
Posters & Infographics
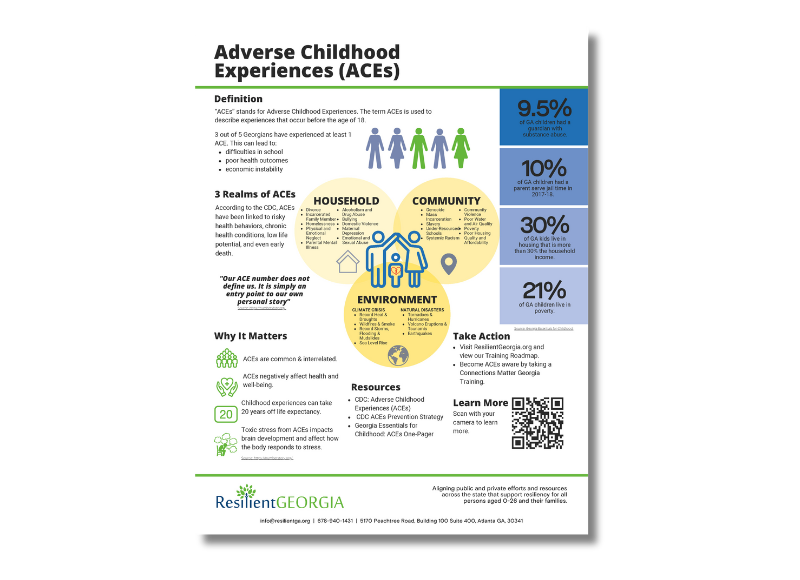
ACEs, Resilience, Toxic Stress Concept Cards

ACEs, Overdose and Suicide Prevention Infographic

